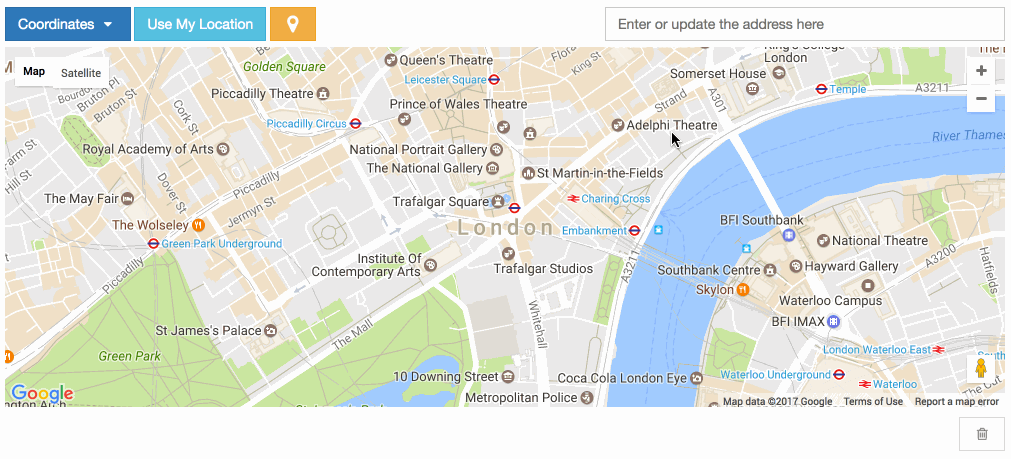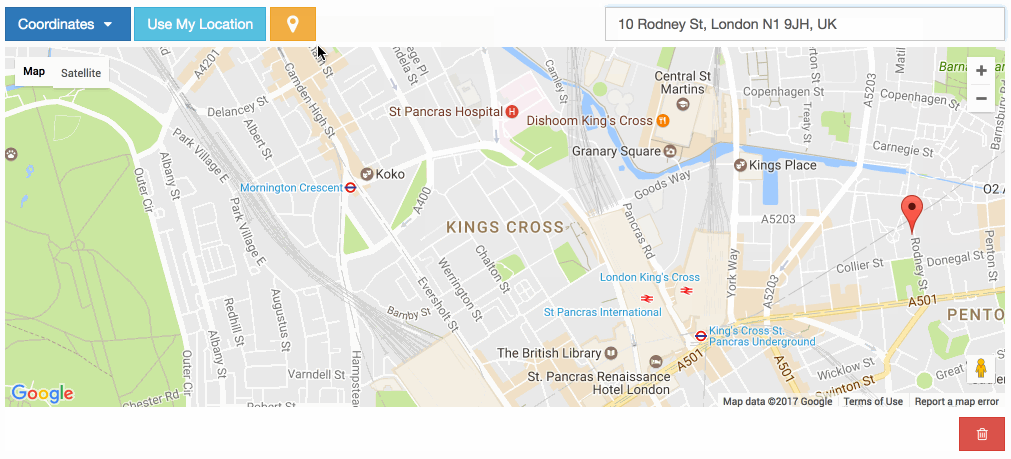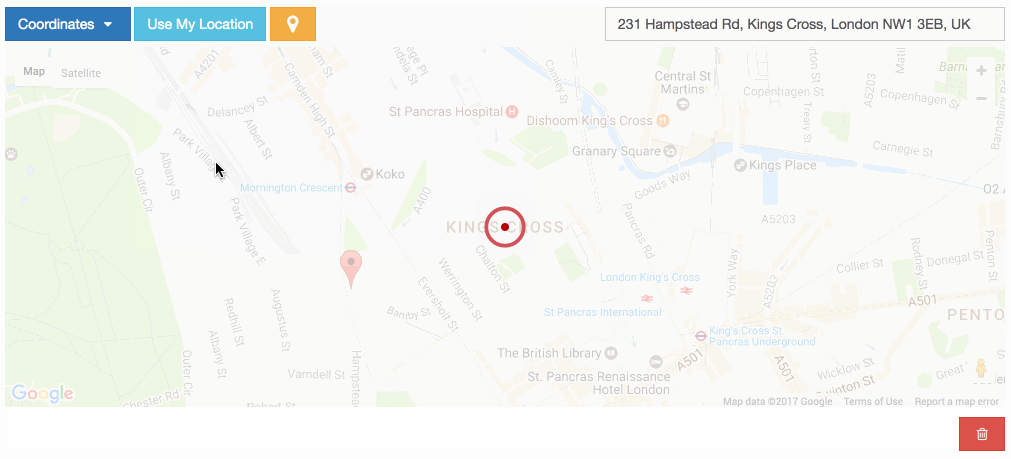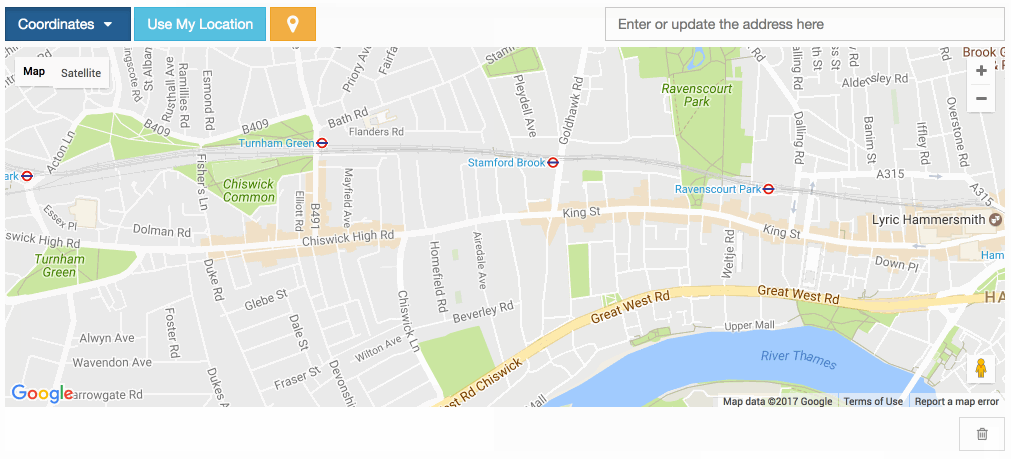
Google Map Point Field Widget¶
Preview¶
Google Map APIs configuration¶
In order to use this widget, you need to enable Google APIs below in your google application configuration;
Tip
The widget has a Google Place Autocomplete component by default. You can find a specific address coordinates with it.
Tip
The widget has built-in geocoding support. The autocomplete input will be filled by google geocoding service when the user adds a marker to map manually.
Settings¶
- GOOGLE_MAP_API_KEY: Put your Google API key (required)
- GOOGLE_MAP_API_SIGNATURE: You can give Google Static Map API signature key (optional). Check out this page.
- LANGUAGE: Google Map language (optional, default value is
en). - mapCenterLocationName: You can give a specific location name for center of the map. Map widget will find this location coordinates using Google Place Autocomplete. (Optional)
- mapCenterLocation: You can give specific coordinates for center of the map. Coordinates must be list type. ([latitude, longitude]) (Optional)
- zoom : Default zoom value for maps (optional, default value is 6).
- scrollWheel : Enables or Disables zooming on the map using a mouse scroll wheel. Set as True in your django settings to enable it, the scroll wheel zooming is disabled by default.
- markerFitZoom : When the marker is initialized google’s default zoom is set to Max. This method sets the zoom level a reasonable distance and center the marker on the map.
- streetViewControl : Whether or not to display the Street View “Peg Man” (optional, default is
True). Setting this toFalseeffectively disables Street View for the widget.
Usage¶
Settings
In your settings.py file, add your MAP_WIDGETS config:
MAP_WIDGETS = {
"GooglePointFieldWidget": (
("zoom", 15),
("mapCenterLocationName", "london"),
("GooglePlaceAutocompleteOptions", {'componentRestrictions': {'country': 'uk'}}),
("markerFitZoom", 12),
("scrollWheel", False),
("streetViewControl", True),
),
"GOOGLE_MAP_API_KEY": "<google-api-key>"
}
If you want to give specific location name or coordinates for center of the map, you can update your settings like that.
MAP_WIDGETS = {
"GooglePointFieldWidget": (
("zoom", 15),
("mapCenterLocation", [57.7177013, -16.6300491]),
),
"GOOGLE_MAP_API_KEY": "<google-map-api-key>"
}
MAP_WIDGETS = {
"GooglePointFieldWidget": (
("zoom", 15),
("mapCenterLocationName", 'Canada'),
),
"GOOGLE_MAP_API_KEY": "<google-map-api-key>"
}
Tip
If there is no specific value set for the map center for mapCenterLocationName, mapCenterLocation the widget will be centred by the timezone setting of the project
Check out these links.
You can also give specific settings as a parameter for each widget.
Note
Google Map is using SRID (Spatial Reference System Identifier) as 4326 as same as Django’s default SRID value for postgis fields. If you are set SRID parameter on a postgis field, the coordinates will store as your SRID format on your database but the widget always converting coordinates to 4326 format when it rendering. Because, the Google Map Javascript API using 4326 format. So, you can see different coordinates values on frontend from your DB but the point will always some location. You can reach more information on this Wikipedia page.
from django.contrib.gis import forms
from mapwidgets.widgets import GooglePointFieldWidget
CUSTOM_MAP_SETTINGS = {
"GooglePointFieldWidget": (
("zoom", 15),
("mapCenterLocation", [60.7177013, -22.6300491]),
),
}
class CityAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
formfield_overrides = {
models.PointField: {"widget": GooglePointFieldWidget(settings=CUSTOM_MAP_SETTINGS)}
}
Note
GOOGLE_MAP_API_KEY must be set in the project Django settings file for custom settings usage.
Django Admin
from mapwidgets.widgets import GooglePointFieldWidget
class CityAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
formfield_overrides = {
models.PointField: {"widget": GooglePointFieldWidget}
}
Django Forms
from mapwidgets.widgets import GooglePointFieldWidget
class CityAdminForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = City
fields = ("coordinates", "city_hall")
widgets = {
'coordinates': GooglePointFieldWidget,
'city_hall': GooglePointFieldWidget,
}
Javascript Triggers¶
If you need to develop your map UI on front-end side, you can use map widget jQuery triggers.
- google_point_map_widget:marker_create: Triggered when user create marker on map. (callback params: place, lat, lng, locationInputElem, mapWrapID)
- google_point_map_widget:marker_change: Triggered when user change marker position on map. (callback params: place, lat, lng, locationInputElem, mapWrapID)
- google_point_map_widget:marker_delete: Triggered when user delete marker on map. (callback params: lat, lng, locationInputElem, mapWrapID)
(function ($){
$(document).on("google_point_map_widget:marker_create", function (e, lat, lng, locationInputElem, mapWrapID) {
console.log("EVENT: marker_create"); // django widget textarea widget (hidden)
console.log(locationInputElem); // django widget textarea widget (hidden)
console.log(lat, lng); // created marker coordinates
console.log(mapWrapID); // map widget wrapper element ID
});
$(document).on("google_point_map_widget:marker_change", function (e, lat, lng, locationInputElem, mapWrapID) {
console.log("EVENT: marker_change"); // django widget textarea widget (hidden)
console.log(locationInputElem); // django widget textarea widget (hidden)
console.log(lat, lng); // changed marker coordinates
console.log(mapWrapID); // map widget wrapper element ID
});
$(document).on("google_point_map_widget:marker_delete", function (e, lat, lng, locationInputElem, mapWrapID) {
console.log("EVENT: marker_delete"); // django widget textarea widget (hidden)
console.log(locationInputElem); // django widget textarea widget (hidden)
console.log(lat, lng); // deleted marker coordinates
console.log(mapWrapID); // map widget wrapper element ID
})
$(document).on("google_point_map_widget:place_changed", function (e, place, lat, lng, locationInputElem, mapWrapID) {
console.log("EVENT: place_changed"); // django widget textarea widget (hidden)
console.log(place); // google geocoder place object
console.log(locationInputElem); // django widget textarea widget (hidden)
console.log(lat, lng); // created marker coordinates
console.log(mapWrapID); // map widget wrapper element ID
});
})(jQuery)
Javascript Objects¶
The widget JS objects googleMapObj and googleMapWidgetObj can reach out via the map HTML elements using with jQuery $.data.
Use jquery selector format like $("#{django-form-field-name}-map-elem") in order to get jquery object. See examples in the demo project templates.